
Dec . 12, 2024 11:17 Back to list
analogue differential pressure gauge product
Understanding Analogue Differential Pressure Gauges
In various industrial applications, the measurement of pressure is crucial for ensuring the safety and efficiency of processes. Among the different types of pressure gauges available, analogue differential pressure gauges play a significant role. This article delves into the functionality, construction, applications, and advantages of these gauges, highlighting their importance in monitoring pressure differences within various systems.
What is an Analogue Differential Pressure Gauge?
An analogue differential pressure gauge is a device used to measure the difference in pressure between two points in a system. Unlike standard pressure gauges that only measure static pressure in one location, differential pressure gauges are designed to provide readings that reflect the pressure difference, allowing for continuous monitoring of pressure variations. This is critical in applications where maintaining a specific pressure differential is vital for smooth operations.
How Does It Work?
The functioning of an analogue differential pressure gauge is based on the principles of pressure transference. It typically consists of two pressure inlets, one connected to each point of the system. These inlets lead to a sensing element, which could be a diaphragm or a Bourdon tube. As pressure is applied, the sensing element deforms, leading to the movement of a pointer on a calibrated dial. The degree of deflection is proportional to the pressure difference between the two points, providing a visual representation of the measurement on the analogue scale.
Construction
Analogue differential pressure gauges are constructed with several key components
1. Sensing Element This is the core component that detects pressure differences. It can be made from various materials depending on the application's specifications, such as stainless steel for corrosive environments.
2. Dial Scale The dial displays the measurement readings. It is calibrated to show the range of differential pressures the gauge can measure, often in units such as psi, bar, or Pascal.
3. Pointer A spring-loaded pointer moves along the dial scale to indicate the pressure difference.
5. Housing The gauge is enclosed in a protective housing that shields it from environmental factors and mechanical damage.
analogue differential pressure gauge product
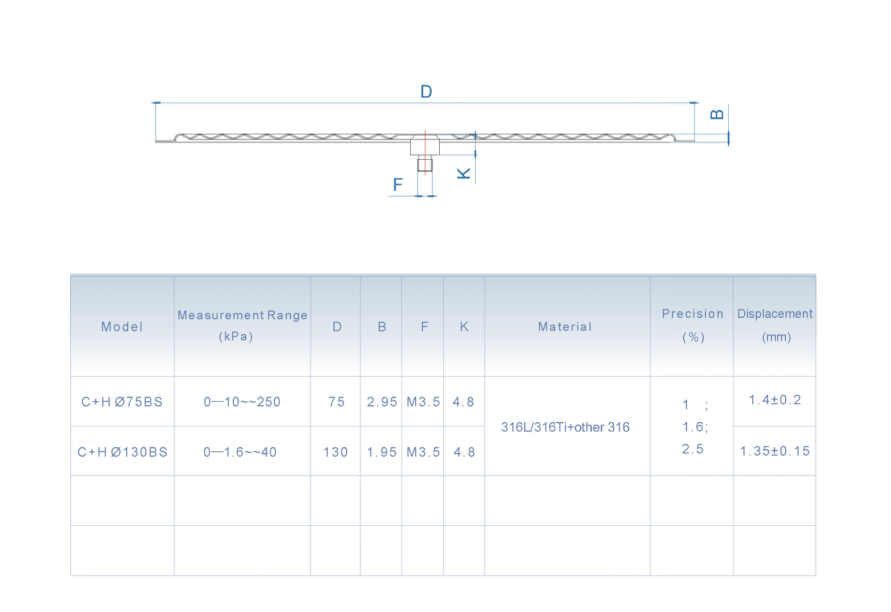
Applications
Analogue differential pressure gauges are used in a variety of fields, including
- HVAC Systems Monitoring filter conditions and ensuring adequate airflow within ducts. - Hydraulics and Pneumatics Assessing pressure drops across valves, pumps, and other components to ensure optimal performance. - Chemical Processing Ensuring that processes operate within safe pressure differentials to prevent chemical spills or reactions. - Water Treatment Monitoring pressure differentials in filtration systems to maintain efficiency.
Advantages
Several advantages make analogue differential pressure gauges popular in many industries
1. Simplicity The simplicity of the design makes them easy to install, operate, and maintain.
2. Cost-Effective Compared to digital alternatives, analogue gauges tend to be more affordable, providing accurate readings without requiring complex electronics.
3. Real-Time Monitoring The analogue display allows for immediate visual checks, making it easier for operators to respond quickly to pressure changes.
4. Durability Many analogue gauges are built to withstand harsh environments, offering long-term reliability in challenging conditions.
5. No Power Requirement Unlike electronic gauges, analogue gauges do not require a power source, making them ideal for remote locations or areas without access to electricity.
Conclusion
In summary, analogue differential pressure gauges are essential instruments in various industrial settings. Their ability to measure pressure differences accurately and reliably contributes significantly to the efficiency and safety of processes across multiple sectors. Understanding their construction, functionality, and applications serves as a key advantage for those looking to optimize their systems and ensure optimal operations. Whether in HVAC systems, hydraulic machinery, or chemical processing plants, these gauges are vital tools that provide robust and straightforward pressure measurement solutions.
-
High-Quality Pressure Gauge on Fire Extinguisher - Reliable Water Fire Extinguisher Pressure Gauge Suppliers & Exporters
NewsJul.08,2025
-
High-Quality Water Pressure Differential and Gauge Kit Reliable Manufacturers & Competitive Quotes
NewsJul.08,2025
-
High-Precision Digital Diaphragm Pressure Gauge – Reliable Manufacturer & Competitive Quotes
NewsJul.07,2025
-
Wholesale Diaphragm Pressure Gauge Supplier - Premium Quality & Competitive Price
NewsJul.07,2025
-
Digital Diaphragm Pressure Gauge Reliable & Precise Measurement Top Manufacturers Quotes
NewsJul.06,2025
-
High Accuracy Piston Type Differential Pressure Gauge - Reliable Manufacturers & Competitive Quotes
NewsJul.06,2025
