
Nov . 26, 2024 23:01 Back to list
Fire Hydrant Pressure Measurement Solutions for Efficient Water Supply Management
Understanding Pressure Gauge Use in Fire Hydrant Systems
Fire hydrants are critical components of urban infrastructure, serving as vital resources for fire protection and emergency response. An essential aspect of ensuring that these hydrants function effectively is the use of pressure gauges. This article explores the importance, types, and maintenance of pressure gauges specific to fire hydrant systems.
The Importance of Pressure Gauges
Pressure gauges play a pivotal role in monitoring and maintaining the water pressure in fire hydrant systems. These instruments provide crucial data that helps fire departments assess the viability and readiness of hydrants during emergencies. A consistent pressure level is necessary to ensure that, during a fire, the hydrant can deliver adequate water supply to combat flames effectively. Insufficient pressure can lead to catastrophic consequences, as firefighters may struggle to obtain the necessary resources at critical moments.
Moreover, pressure gauges help municipalities and water departments identify potential problems within the water supply system. For example, a drop in pressure could indicate leaks, blockages, or other issues that need immediate attention. Regular monitoring through these gauges can help maintain the integrity and performance of the entire firefighting system.
Types of Pressure Gauges
There are several types of pressure gauges used in fire hydrants, each serving specific functions
1. Mechanical Pressure Gauges These are the most common type, utilizing a dial to display pressure readings. They operate based on the movement of a spring mechanism, which reacts to changes in pressure. Mechanical gauges are reliable and require minimal maintenance, making them a staple in many firefighting systems.
2. Digital Pressure Gauges Digital gauges provide more accurate and easy-to-read measurements. They can display real-time data and are often equipped with features such as alarms for pressure fluctuations. Although they can be more expensive, the precision they offer can be invaluable in critical situations.
pressure gauge for fire hydrant companies
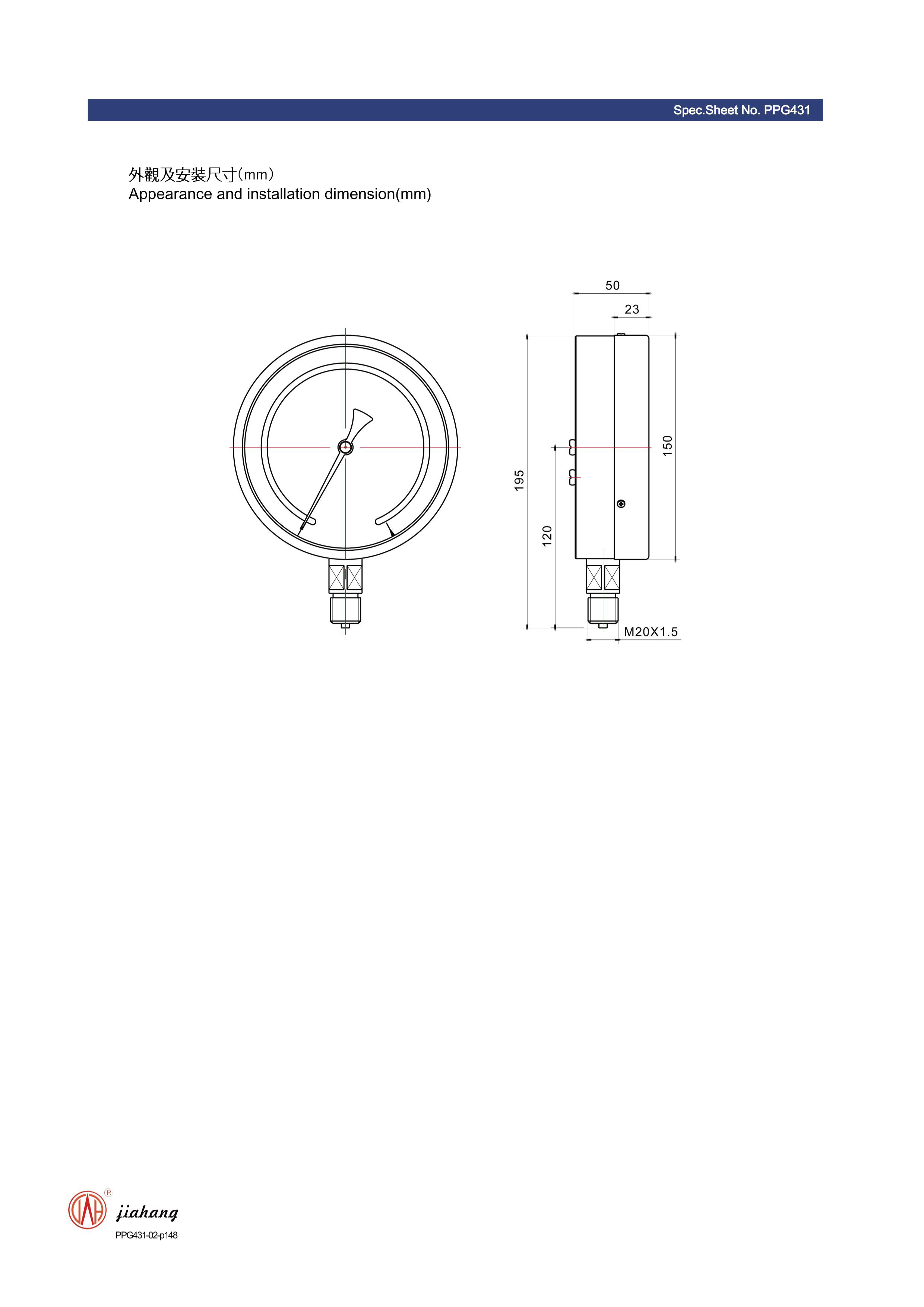
3. Data Logging Pressure Gauges These advanced gauges not only measure pressure but also record it over time. This functionality is useful for long-term monitoring of hydrant performance and identifying trends or potential issues that might not be evident from real-time measurements alone.
Maintenance of Pressure Gauges
For pressure gauges to function accurately, regular maintenance is required. Here are some best practices
- Routine Calibration Ensuring that pressure gauges are calibrated to maintain accuracy is crucial. Municipalities should establish a regular calibration schedule, typically at least once a year or according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Visual Inspections Regular visual inspections can help identify any physical damage or wear on the gauge. Signs of rust, leaks, or broken parts should be addressed immediately.
- Testing Under Pressure Conducting tests under actual working pressures can help verify that gauges provide accurate readings. This procedure is essential, especially after any repairs or replacements within the hydrant system.
- Documentation Keeping detailed records of maintenance activities, calibrations, and inspections can help track the performance and reliability of each gauge over time.
Conclusion
Incorporating pressure gauges into fire hydrant systems is essential for ensuring their efficiency and reliability. With proper monitoring and maintenance, these instruments not only enhance firefighting capabilities but also contribute to the overall safety of communities. As urban areas continue to grow and infrastructure demands increase, the role of pressure gauges in fire hydrant systems will remain indispensable. By prioritizing their upkeep, municipalities can ensure that firefighters are equipped with the resources they need during emergencies, ultimately safeguarding lives and property.
-
High-Precision Mass Diaphragm Pressure Gauge - Reliable & Durable Solutions
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Explain Diaphragm Pressure Gauge Expert Guide, Top Manufacturers & Quotes
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Affordable Differential Pressure Gauge Prices in China Top Manufacturers
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Reliable Water Fire Extinguisher Pressure Gauges for Safety
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Durable Diaphragm Protection Pressure Gauges Get Quote
NewsJun.09,2025
-
WIKA Differential Pressure Gauge with Switch Reliable Monitoring & Control
NewsJun.09,2025
