
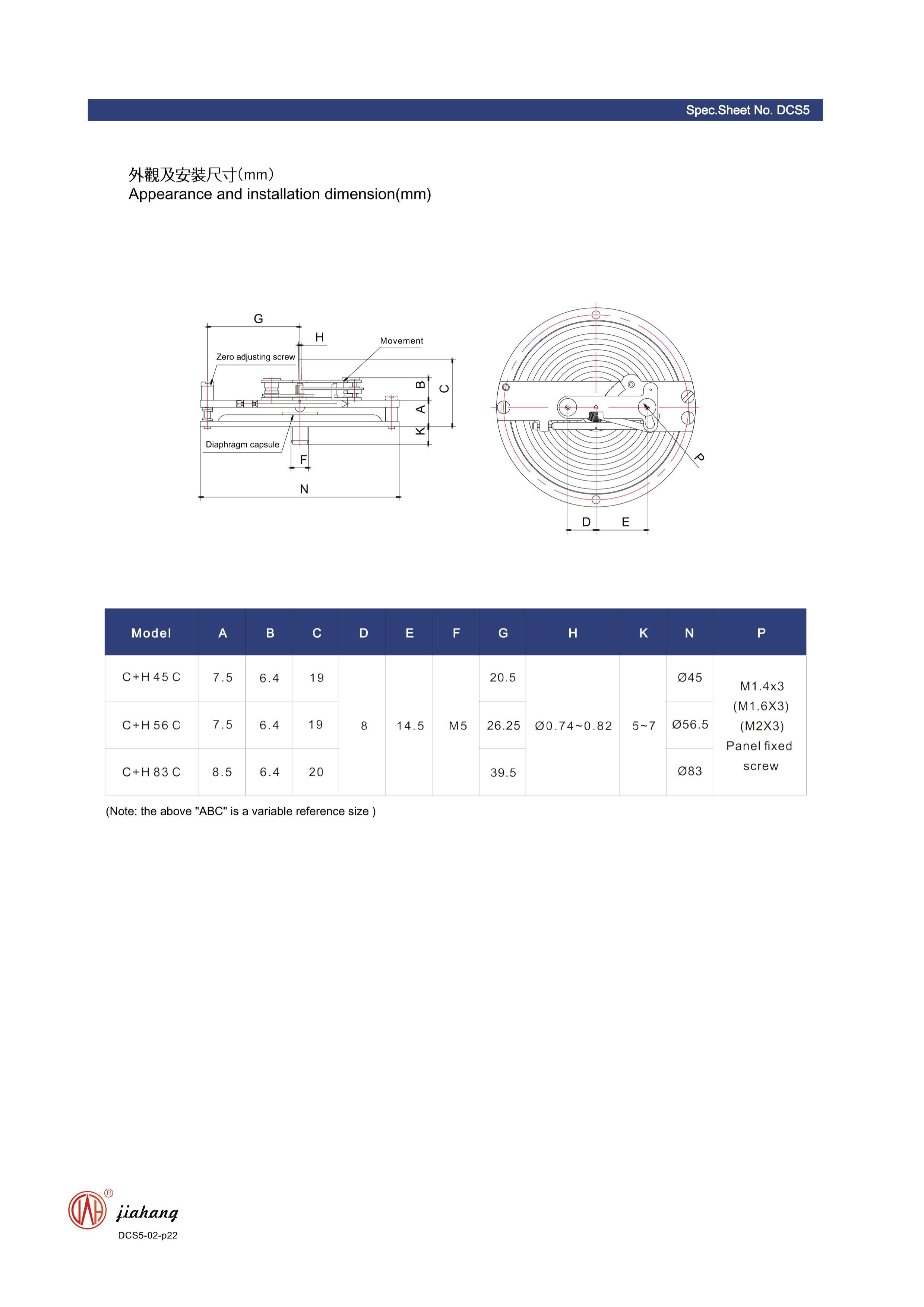
Nov . 06, 2024 07:12 Back to list
Medical Pressure Gauge Measurements in Centimeters of Water Column for Healthcare Applications
Understanding Medical Pressure Gauges A Focus on cm H2O
In the medical field, accurate measurement of pressure is vital for assessing various physiological states and ensuring effective treatments. One unit often used in this context is the centimeter of water (cm H2O), which serves as a standard for measuring pressures in medical settings, particularly when dealing with respiratory and cardiovascular systems. This article explores the significance of medical pressure gauges, specifically focusing on cm H2O, and their vital role in patient care.
What is a Medical Pressure Gauge?
A medical pressure gauge is an instrument used to measure the pressure of fluids or gases within a system. These gauges are essential in numerous applications, from monitoring blood pressure in patients to assessing the functionality of ventilators and other respiratory devices. Medical pressure gauges can present measurements in various units, including millimeters of mercury (mmHg), pascals (Pa), and centimeters of water (cm H2O). The choice of unit often depends on the specific requirements of the medical procedure being conducted.
The Importance of cm H2O
The unit cm H2O measures pressure based on the height of a column of water that a certain atmospheric force can support. Specifically, one cm H2O is equivalent to the pressure exerted by a 1 cm column of water at standard gravity. This unit is particularly useful in medical contexts because it offers a clear and comprehensible scale for clinicians, especially when dealing with low-pressure ranges typical in respiratory measurements.
For instance, normal atmospheric pressure is approximately 1013.25 hPa, which translates to about 1033 cm H2O. However, for measuring pressures within the human body, much lower values are typically encountered. For example, a blood pressure gauge may report pressures around 120/80 mmHg, equivalent to approximately 162/107 cm H2O—illustrating why cm H2O is an appropriate choice for many medical applications.
medical pressure gauge cm h2o jah
Applications in Medicine
One of the most common applications of cm H2O is in respiratory care. Medical professionals frequently use pressure gauges to monitor airflow within ventilators and CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure) machines. These devices help individuals with breathing difficulties by providing a steady airflow, and clinicians must monitor the pressure to ensure efficacy and safety.
In ventilatory support, measuring against cm H2O helps clinicians evaluate the effectiveness of the ventilatory strategy. If the pressure in the ventilation system is too low, it may not deliver adequate oxygen to the patient, leading to potential complications. Conversely, excessive pressure can cause lung injury. Therefore, maintaining the right balance through accurate measurement is critical.
In addition to respiratory applications, cm H2O is also relevant in assessing intracranial pressure (ICP). Elevated ICP can indicate serious medical conditions such as traumatic brain injury or hydrocephalus. Continuous monitoring of ICP often involves using specialized pressure gauges that can accurately convey pressures in cm H2O.
Conclusion
The significance of cm H2O in medical pressure gauges cannot be overstated. It provides a straightforward measure for evaluating pressures in various healthcare settings, particularly in respiratory and cardiology applications. Clinicians rely on these instruments to make informed decisions about treatments, ensuring that therapies are tailored to meet the individual needs of each patient. By understanding and utilizing cm H2O measurements, health professionals can enhance patient care outcomes and maintain the highest standards of medical practice. With ongoing advancements in technology and methodology, the role of precise pressure measurement will continue to evolve, further solidifying the importance of understanding medical pressure gauges.
-
High-Precision Mass Diaphragm Pressure Gauge - Reliable & Durable Solutions
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Explain Diaphragm Pressure Gauge Expert Guide, Top Manufacturers & Quotes
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Affordable Differential Pressure Gauge Prices in China Top Manufacturers
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Reliable Water Fire Extinguisher Pressure Gauges for Safety
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Durable Diaphragm Protection Pressure Gauges Get Quote
NewsJun.09,2025
-
WIKA Differential Pressure Gauge with Switch Reliable Monitoring & Control
NewsJun.09,2025
