
Dec . 12, 2024 04:28 Back to list
famous types of differential pressure gauges
Famous Types of Differential Pressure Gauges
Differential pressure gauges are essential instruments used in various industries to measure the difference in pressure between two points. They play a critical role in ensuring the efficient functioning of systems, including HVAC, chemical processing, oil and gas, and water treatment, among others. By providing accurate and reliable measurements, these gauges help maintain optimal operational conditions, detect leaks, and prevent equipment failures. In this article, we will explore some of the most famous types of differential pressure gauges and their applications.
1. Bourdon Tube Differential Pressure Gauge
One of the most widely used types of differential pressure gauges is the Bourdon tube gauge. This device consists of a curved tube that straightens as pressure increases. The differential pressure between two points acts on the tube, causing it to bend, which in turn moves a needle on a calibrated dial. Known for its simplicity and reliability, the Bourdon tube gauge can measure high pressures and is often employed in process industries. Its robust construction makes it suitable for harsh conditions, but it is less effective for very low pressure measurements.
2. Diaphragm Differential Pressure Gauge
The diaphragm differential pressure gauge utilizes a flexible diaphragm that separates the two pressure points. When pressure is applied, the diaphragm deflects, and this movement is transmitted to a magnetic or mechanical indicator, which displays the differential pressure. Because of their sensitivity, diaphragm gauges are preferred for low-pressure measurements and applications like gas and liquid flow monitoring. They also provide excellent performance in corrosive environments by utilizing materials such as stainless steel, PTFE, or other resistant materials for the diaphragm.
3. Capillary Differential Pressure Gauge
Capillary differential pressure gauges incorporate a flexible tube or capillary between two pressure points, which is often filled with a liquid. The variations in pressure produce a change in liquid levels, which is converted into a differential pressure reading. These gauges are especially useful in applications where the pressure sources are far apart or located in hazardous areas. They offer high accuracy and can be used in various process industries, including pharmaceuticals and food processing.
famous types of differential pressure gauges
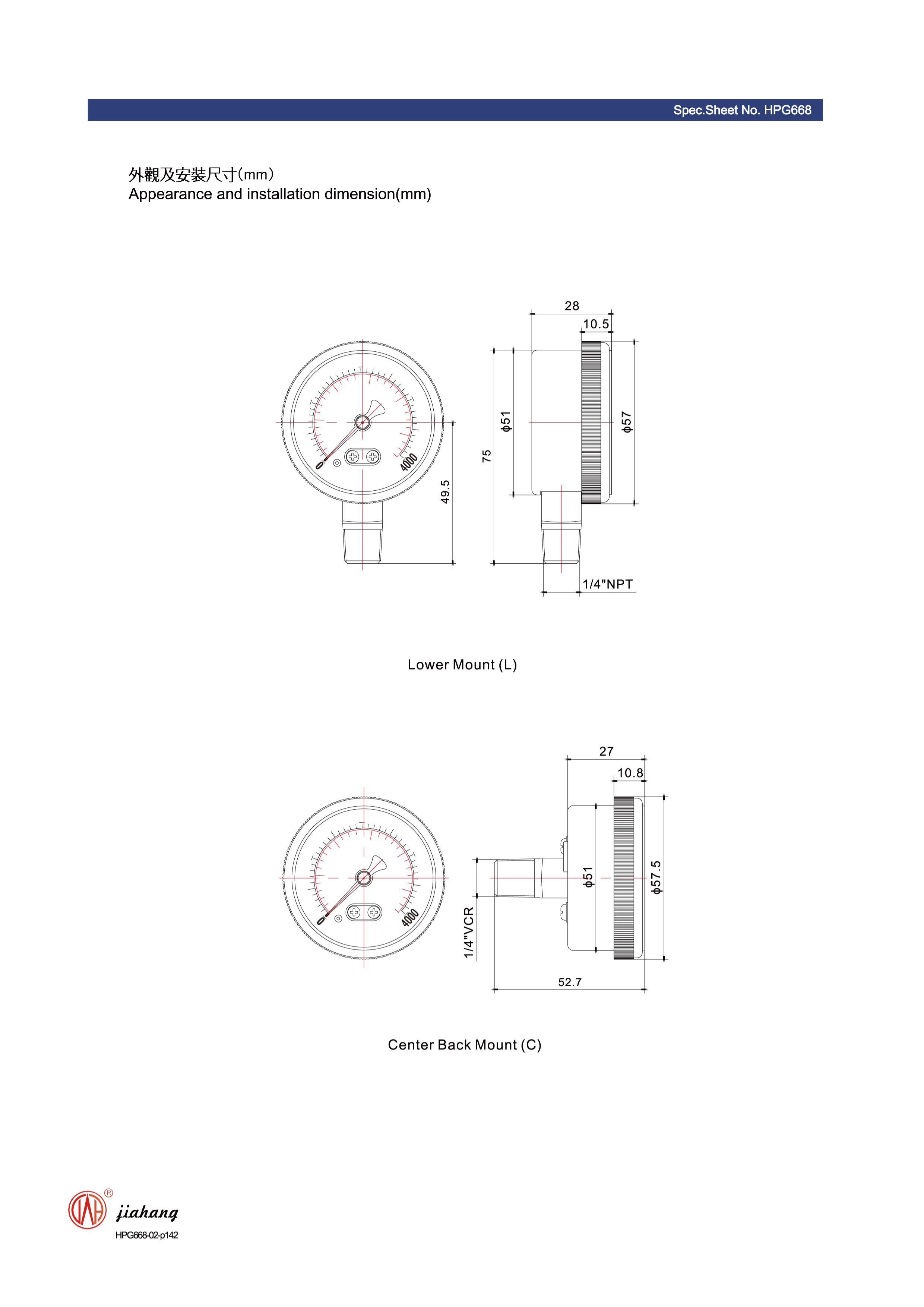
4. Electronic Differential Pressure Gauge
With advancements in technology, electronic differential pressure gauges have gained popularity. These devices employ electronic sensors to measure pressure differences, providing digital outputs that can be easily read and recorded. They offer high precision and can be integrated with control systems for real-time monitoring and data logging. Many electronic gauges also come with features like alarms, remote communication, and calibration options. Their versatility makes them suitable for diverse applications, including energy management and environmental monitoring.
5. Manometer Differential Pressure Gauge
Manometers are simple devices that measure pressure differences using a fluid column. They can be U-tube manometers or single-column manometers, typically filled with water or mercury. In a U-tube manometer, the height difference in the fluid columns is proportional to the pressure differential between the two points. While manometers may not be as commonly used in industrial settings due to their size and the need for a stable environment, they are valuable for low-pressure applications in laboratories and educational demonstrations.
Applications of Differential Pressure Gauges
Differential pressure gauges are utilized across various sectors for a wide range of applications, including
- HVAC Systems These gauges help monitor air pressure differences in ventilation systems, ensuring optimal airflow and energy efficiency. - Filtration Processes By measuring the pressure drop across filters, these instruments indicate when a filter needs to be replaced or cleaned, thus maintaining system performance. - Level Measurement In tanks and reactors, differential pressure gauges can be used to measure the level of liquid, contributing to effective process management. - Flow Measurement Differential pressure is essential for flow measurement applications, such as those utilizing orifice plates or flow nozzles.
In conclusion, differential pressure gauges are vital tools across various industries, providing insights into system performance and enhancing operational efficiency. The diverse array of types, from mechanical Bourdon tube gauges to advanced electronic models, ensures that there are options suited for nearly every application and environment. Understanding the differences among these gauges allows engineers and technicians to select the most appropriate gauge for their specific needs, ultimately leading to safer and more efficient operations.
-
High-Quality Pressure Gauge on Fire Extinguisher - Reliable Water Fire Extinguisher Pressure Gauge Suppliers & Exporters
NewsJul.08,2025
-
High-Quality Water Pressure Differential and Gauge Kit Reliable Manufacturers & Competitive Quotes
NewsJul.08,2025
-
High-Precision Digital Diaphragm Pressure Gauge – Reliable Manufacturer & Competitive Quotes
NewsJul.07,2025
-
Wholesale Diaphragm Pressure Gauge Supplier - Premium Quality & Competitive Price
NewsJul.07,2025
-
Digital Diaphragm Pressure Gauge Reliable & Precise Measurement Top Manufacturers Quotes
NewsJul.06,2025
-
High Accuracy Piston Type Differential Pressure Gauge - Reliable Manufacturers & Competitive Quotes
NewsJul.06,2025
