
Dec . 14, 2024 16:31 Back to list
differential pressure gauge p& quotes
Understanding Differential Pressure Gauges Principle, Applications, and Selection
Differential pressure gauges are essential instruments used in various industries to measure the pressure difference between two points in a system. Their functionality is vital for ensuring the efficiency, safety, and reliability of processes in sectors such as oil and gas, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning).
Principle of Operation
At the core of the differential pressure gauge is its ability to measure the difference in pressure between two specified locations, typically denoted as high and low pressure ports. The gauge operates on the principle that pressure can be viewed as a force per unit area. When the pressures at these two ports differ, the resultant force creates a displacement in a sensing element, which could be a diaphragm or a bourdon tube, depending on the gauge's design.
The differential pressure is primarily exhibited on a dial or digital display, providing operators with valuable information about system performance. The gauges are often calibrated to provide accurate readings, ensuring that operators can respond quickly to changes in pressure, which may indicate a blockage, filter clogging, or other operational issues.
Applications
Differential pressure gauges find applications in numerous fields
1. HVAC Systems They are employed to monitor air filters and ducts to ensure that airflow remains at optimal levels. A significant rise in differential pressure can indicate a clogged filter, prompting maintenance before system efficiency is compromised.
2. Process Industries In chemical and petrochemical manufacturing, they are vital for monitoring flow rates and ensuring that processes remain within specific pressure limits. Deviations in pressure can lead to safety hazards, hence the need for accurate monitoring.
3. Pharmaceutical Industry In sterile environments, maintaining the integrity of cleanrooms is critical. Differential pressure gauges help ensure that the pressure differential between clean areas and non-clean areas is maintained to prevent contamination.
differential pressure gauge p& quotes
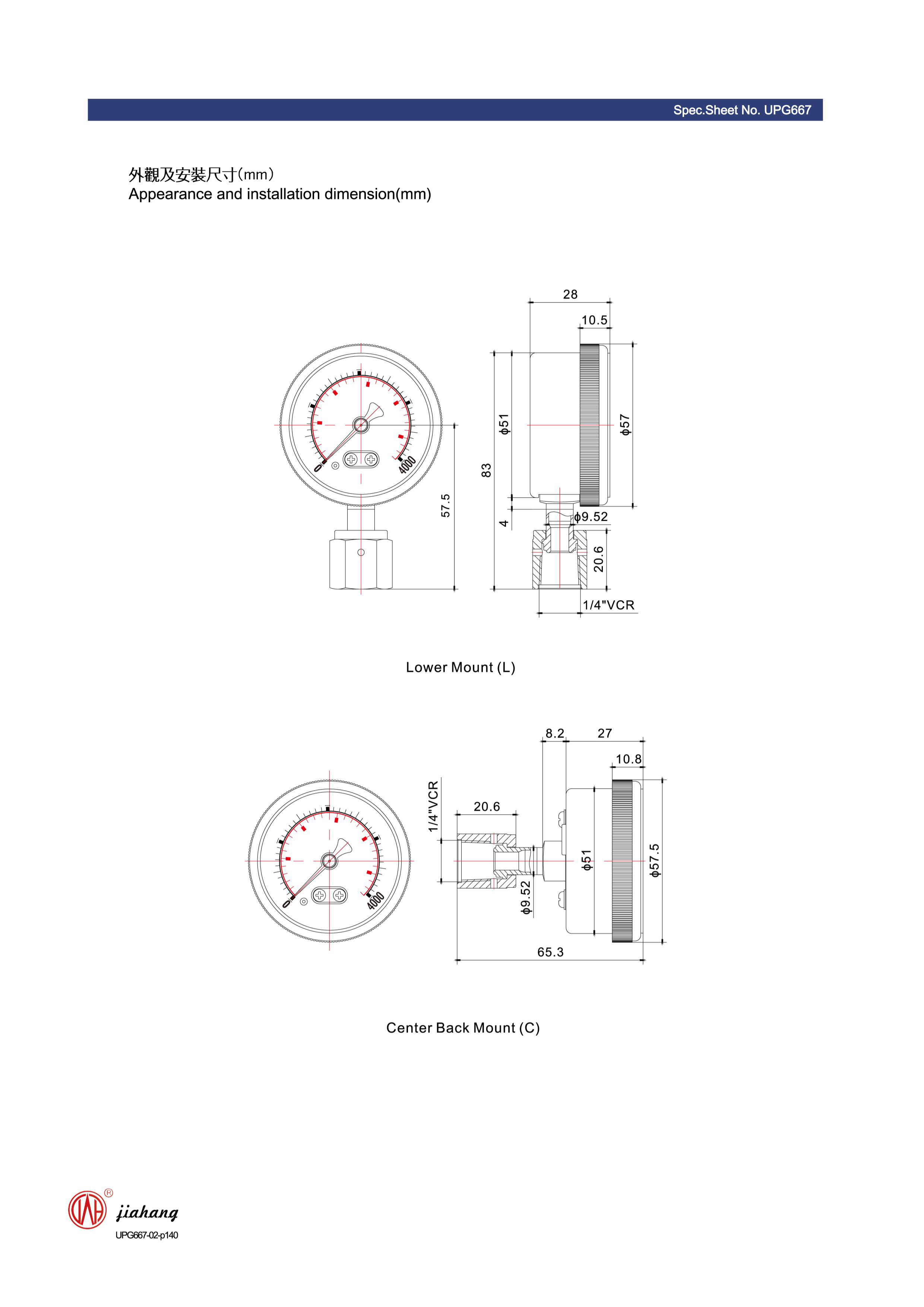
4. Water and Wastewater Management These gauges are used to measure pressure drops across filters and membranes, helping to assess filter performance and system integrity.
Selection Criteria
When selecting a differential pressure gauge, several factors should be taken into consideration
- Measurement Range It's crucial to choose a gauge that suits the expected range of differential pressures. Operating far from the specified range can lead to inaccurate readings or damage to the gauge.
- Accuracy Class Depending on the application, the accuracy of the gauge can be critical. High-precision tasks in pharmaceuticals may require gauges with a tighter accuracy tolerance compared to general use in HVAC systems.
- Construction Materials Depending on the media being measured (liquid, gas, corrosive substances), the materials of construction will vary. Choosing a gauge with compatible materials is important for durability and accuracy.
- Output Signal For integration with control systems, differential pressure gauges can come with various output signals (e.g., 4-20 mA, digital readouts) compatible with monitoring systems.
- Environment Operating conditions such as temperature, humidity, and presence of dust or chemicals in the environment can affect gauge performance. Selecting a gauge rated for the expected environmental conditions is essential.
Conclusion
Differential pressure gauges are pivotal instruments across many industries, providing critical insights into system performance and safety. Understanding their workings, applications, and selection criteria can significantly enhance operational efficiency and prevent costly downtime. Whether monitoring HVAC systems, ensuring pharmaceutical protocols, or maintaining industrial processes, these gauges play a vital role in contemporary engineering solutions. The right selection and proper maintenance of differential pressure gauges ensure that they contribute effectively to operational success and safety.
-
High-Quality Pressure Gauge on Fire Extinguisher - Reliable Water Fire Extinguisher Pressure Gauge Suppliers & Exporters
NewsJul.08,2025
-
High-Quality Water Pressure Differential and Gauge Kit Reliable Manufacturers & Competitive Quotes
NewsJul.08,2025
-
High-Precision Digital Diaphragm Pressure Gauge – Reliable Manufacturer & Competitive Quotes
NewsJul.07,2025
-
Wholesale Diaphragm Pressure Gauge Supplier - Premium Quality & Competitive Price
NewsJul.07,2025
-
Digital Diaphragm Pressure Gauge Reliable & Precise Measurement Top Manufacturers Quotes
NewsJul.06,2025
-
High Accuracy Piston Type Differential Pressure Gauge - Reliable Manufacturers & Competitive Quotes
NewsJul.06,2025
