
Nov . 16, 2024 09:50 Back to list
differential pressure gauge assembly jah
Understanding Differential Pressure Gauge Assembly A Comprehensive Overview
Differential pressure gauge assemblies are critical instruments in various industrial applications, ranging from HVAC systems to oil and gas processes. These gauges measure the difference in pressure between two points, providing vital information that helps in controlling processes, monitoring equipment performance, and ensuring safety. This article delves into the components, functioning, and applications of differential pressure gauge assemblies.
Components of a Differential Pressure Gauge Assembly
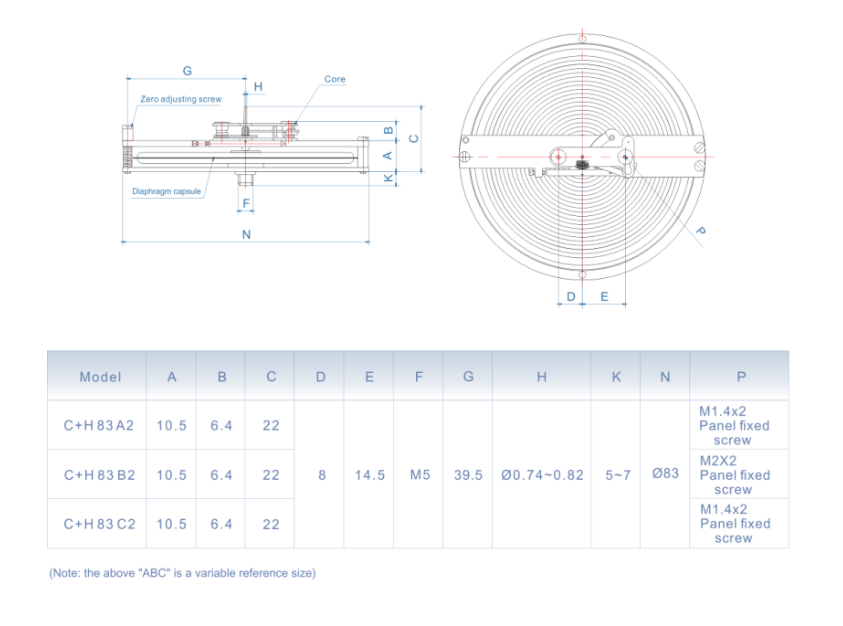
A typical differential pressure gauge assembly consists of several key components
1. Pressure Sensors At the heart of the assembly are two pressure sensors that measure the pressure at different points in the system. These sensors can be mechanical (Bourdon tube type) or electronic (piezoelectric or capacitive sensors), depending on the accuracy and sensitivity required.
2. Display Unit The display unit translates the sensor readings into a comprehensible format, often indicated in units such as psi (pounds per square inch), bar, or kPa (kilopascals). Modern units may also feature digital displays and programmable settings.
3. Connection Ports These are ports where the pressure sensing elements connect to the process lines. The design of connection ports ensures a leak-proof seal, which is crucial for accurate pressure measurement.
4. Calibration Mechanisms Calibration is essential for ensuring the accuracy of differential pressure measurements. Most assemblies come with built-in calibration mechanisms allowing for easy adjustments to maintain precision over time.
5. Housing and Protection The entire assembly is typically housed in a durable casing designed to protect the components from environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and extreme temperatures.
Functioning of Differential Pressure Gauges
differential pressure gauge assembly jah
The differential pressure gauge measures pressure differences by taking readings from two points within a system. When pressure is applied to one sensor, the mechanical or electronic system detects this change and compares it with the reading from the other sensor. The difference is then calculated and displayed, providing insights into system performance.
These gauges are particularly effective in systems where fluid flow or pressure changes need to be monitored. By analyzing the differential pressure, operators can infer the condition of filters, pumps, and other equipment. For instance, a significant drop in pressure across a filter may indicate that it is clogged and requires cleaning or replacement.
Applications of Differential Pressure Gauge Assemblies
Differential pressure gauges find application across numerous sectors
1. HVAC Systems In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, differential pressure gauges are used to monitor air filters and duct pressures. This helps in maintaining optimal performance and energy efficiency.
2. Oil and Gas Industry These gauges are crucial in monitoring pipeline pressures and ensuring safety. They help in detecting leaks and controlling the flow of materials.
3. Water and Wastewater Management Differential pressure gauges are employed in monitoring the performance of pumps and assessing the level of filtration systems, ensuring efficient water treatment processes.
4. Pharmaceutical and Food Processing In industries where hygiene and contamination prevention are paramount, differential pressure gauges help monitor cleanroom conditions and validate the performance of sterilization processes.
Conclusion
Differential pressure gauge assemblies play a vital role in ensuring the efficiency, safety, and reliability of various industrial processes. Their ability to measure pressure differences accurately makes them indispensable in a wide range of applications. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even greater accuracy and functionality in these essential instruments, contributing to improved operational standards across industries. Understanding how they work and their applications can significantly impact operational success and safety in any facility.
-
High-Precision Mass Diaphragm Pressure Gauge - Reliable & Durable Solutions
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Explain Diaphragm Pressure Gauge Expert Guide, Top Manufacturers & Quotes
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Affordable Differential Pressure Gauge Prices in China Top Manufacturers
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Reliable Water Fire Extinguisher Pressure Gauges for Safety
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Durable Diaphragm Protection Pressure Gauges Get Quote
NewsJun.09,2025
-
WIKA Differential Pressure Gauge with Switch Reliable Monitoring & Control
NewsJun.09,2025
