
Oct . 31, 2024 06:50 Back to list
diaphragm material pressure gauge manufacturers
Diaphragm Material in Pressure Gauge Manufacturing
In the manufacturing of pressure gauges, the choice of diaphragm material plays a critical role in ensuring the accuracy, durability, and reliability of the measurement instrument. A pressure gauge is designed to measure the pressure of gases or liquids in various industrial applications. The diaphragm is the heart of the gauge, as it responds to changes in pressure, converting them into mechanical movement that can be read on a dial or a digital display.
One of the most commonly used materials for diaphragms in pressure gauges is stainless steel. Its excellent mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand high pressures make it an ideal choice for a wide range of applications, including oil, gas, and chemical processing. Stainless steel diaphragms can provide reliable performance in harsh environments, ensuring longevity and consistent readings.
Another important material is silicone rubber. Silicone diaphragms are especially valuable in applications where flexibility and low-temperature performance are required. They are often used in food and pharmaceutical industries, where hygiene and the ability to handle varying temperatures are crucial. Silicone's inert nature ensures that it does not react with the substances being measured, making it a safe choice for sensitive applications.
diaphragm material pressure gauge manufacturers
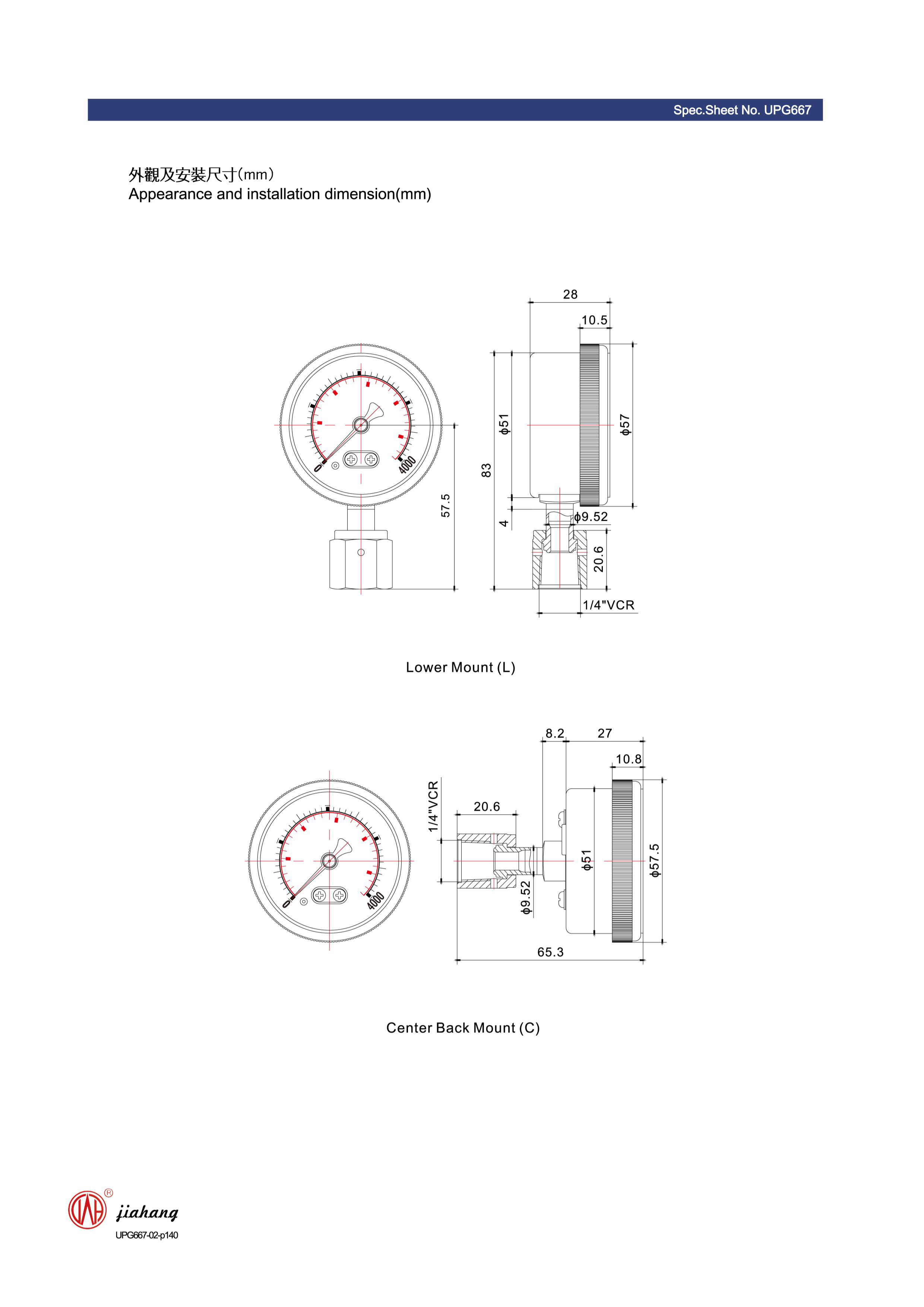
Monel, a nickel-copper alloy, is also an excellent option for diaphragm manufacturing. It demonstrates outstanding resistance to corrosive environments, particularly in marine applications or with aggressive chemicals. Manufacturers often prefer Monel for its durability and performance in extreme conditions, ensuring that the pressure gauge can maintain accuracy and functionality over time.
In recent years, advancements in materials science have led to the development of composite and specialized alloys for diaphragm use. These materials aim to enhance the sensitivity and breadth of measuring range of pressure gauges while minimizing the risk of fatigue and failure over prolonged use. For instance, the latest innovations include the use of polymers and engineered plastics that offer a lightweight alternative without compromising on performance.
Selecting the appropriate diaphragm material is essential not only for accuracy but also for safety. In high-pressure applications, a diaphragm failure could lead to hazardous situations, making the integrity of the material paramount. Manufacturers must consider the specific requirements of the intended application, including pressure range, fluid characteristics, temperature fluctuations, and environmental factors, when designing a pressure gauge.
In conclusion, the diaphragm material is a foundational aspect of pressure gauge manufacturing. With options ranging from stainless steel and silicone to specialized alloys, manufacturers can tailor their products to meet a wide array of industrial needs. As technology continues to evolve, the pressure gauge industry will likely see further innovations in diaphragm materials, enhancing performance, safety, and effectiveness across various applications.
-
High-Precision Mass Diaphragm Pressure Gauge - Reliable & Durable Solutions
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Explain Diaphragm Pressure Gauge Expert Guide, Top Manufacturers & Quotes
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Affordable Differential Pressure Gauge Prices in China Top Manufacturers
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Reliable Water Fire Extinguisher Pressure Gauges for Safety
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Durable Diaphragm Protection Pressure Gauges Get Quote
NewsJun.09,2025
-
WIKA Differential Pressure Gauge with Switch Reliable Monitoring & Control
NewsJun.09,2025
