
Dec . 17, 2024 16:37 Back to list
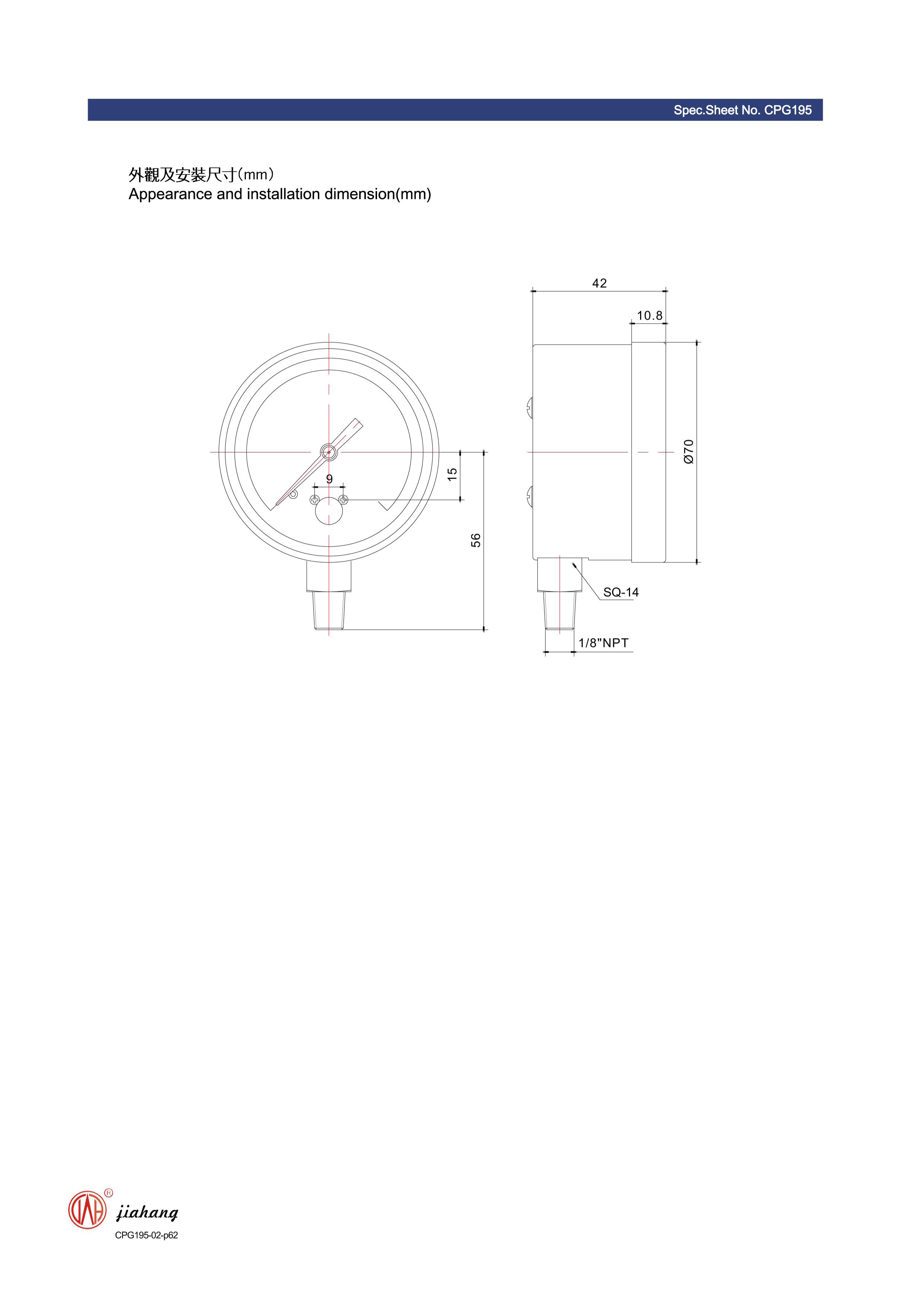
a diaphragm type pressure gauge
Understanding Diaphragm Type Pressure Gauges
Pressure measurement is an essential aspect of various industries, including manufacturing, oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, and many others. One of the most effective methods for measuring pressure is through the use of diaphragm type pressure gauges. This article explores the construction, working principle, advantages, disadvantages, and applications of diaphragm type pressure gauges.
Construction of Diaphragm Type Pressure Gauges
A diaphragm type pressure gauge typically consists of a metallic housing, a flexible diaphragm, and a mechanism to convert the diaphragm’s deflection into a pressure reading. The diaphragm, usually made of stainless steel or other resilient materials, is situated within the pressure gauge and is sealed to form a chamber. This chamber is connected to the pressure source, allowing the diaphragm to deform when pressure is applied.
The deformation of the diaphragm translates into mechanical movement, which is then linked to a pointer or digital readout to display the pressure reading. The gauge may also incorporate various additional features, such as valves for zero adjustment, protective covers, and electrical signal outputs for automated processes.
Working Principle
The working principle of a diaphragm type pressure gauge is based on the mechanical deformation of the diaphragm when exposed to pressure. When pressure is applied to one side of the diaphragm, it flexes, and this deflection is proportional to the pressure exerted. The amount of bend is detected by a mechanism—usually a set of gears or a transducer—that converts this mechanical motion into a readable format.
In analog models, this mechanical motion drives a needle across a calibrated scale, providing a visual indication of the pressure. In digital models, electronic sensors interpret the diaphragm's displacement, converting it into electrical signals that can be processed and displayed numerically.
Advantages of Diaphragm Type Pressure Gauges
One of the key advantages of diaphragm type pressure gauges is their versatility. They can be used to measure both low and high pressures, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. The diaphragm can also isolate the gauge from the medium being measured, which prevents contamination and reduces wear on the internal components.
a diaphragm type pressure gauge
Another significant benefit is the gauge's ability to handle viscous or corrosive fluids. Since the diaphragm can be manufactured from a variety of materials, gauges can be designed to withstand harsh environments while maintaining accuracy. Diaphragm gauges are also relatively compact, making them easy to integrate into various systems without requiring extensive space.
Disadvantages of Diaphragm Type Pressure Gauges
Despite their numerous advantages, diaphragm type pressure gauges do have some drawbacks. One limitation is their susceptibility to mechanical damage due to extreme pressures or impacts. Over time, repeated exposure to fluctuating pressures or environmental conditions can also lead to fatigue and deformation of the diaphragm, which could potentially affect accuracy.
Moreover, while they are suitable for many applications, diaphragm gauges may not be ideal for high-pressure situations above their rated capacity, where other types of pressure gauges, such as Bourdon tube gauges, might perform better. Additionally, the cost of diaphragm gauges can be higher compared to simpler gauge types, which could be a consideration for budget-conscious applications.
Applications of Diaphragm Type Pressure Gauges
Diaphragm type pressure gauges are widely used across many industries due to their robustness and reliability. In the oil and gas industry, they are frequently employed to monitor pressures in various processes, including extraction and refinement. In the pharmaceutical sector, diaphragm gauges help ensure that products are manufactured under the correct pressure conditions, maintaining quality and safety standards.
Furthermore, these gauges are found in HVAC systems, where they measure gas pressures to optimize heating and cooling processes. Their ability to handle corrosive and viscous fluids also makes them suitable for use in chemical processing and wastewater management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, diaphragm type pressure gauges play a crucial role in pressure measurement across various industries. Their unique construction and operating principles allow for accurate and reliable pressure readings in both challenging and standard environments. While they have some limitations, the advantages they offer, particularly in terms of versatility and robustness, make them an essential tool for many applications. Understanding their functionality, advantages, and appropriate usage helps industries maintain efficiency and safety in their operations.
-
High-Quality Pressure Gauge on Fire Extinguisher - Reliable Water Fire Extinguisher Pressure Gauge Suppliers & Exporters
NewsJul.08,2025
-
High-Quality Water Pressure Differential and Gauge Kit Reliable Manufacturers & Competitive Quotes
NewsJul.08,2025
-
High-Precision Digital Diaphragm Pressure Gauge – Reliable Manufacturer & Competitive Quotes
NewsJul.07,2025
-
Wholesale Diaphragm Pressure Gauge Supplier - Premium Quality & Competitive Price
NewsJul.07,2025
-
Digital Diaphragm Pressure Gauge Reliable & Precise Measurement Top Manufacturers Quotes
NewsJul.06,2025
-
High Accuracy Piston Type Differential Pressure Gauge - Reliable Manufacturers & Competitive Quotes
NewsJul.06,2025
